Introduction
Ensuring food safety is a top priority in food processing. The challenge lies in selecting the right technology to detect foreign contaminants like metal, glass, or stones that could compromise product integrity. Metal detection and X-ray inspection are two common methods used to ensure contaminants are identified and removed efficiently. In this article, we will discuss the strengths and applications of both technologies. By the end, you will understand which method best suits your facility’s needs.
Understanding Metal Detection and X-ray Inspection
What is Metal Detection?
Metal detection works by using electromagnetic fields to identify metal contaminants. The system generates a magnetic field through coils, and when metal objects pass through, they disrupt this field, triggering an alarm. Metal detectors can detect ferrous (iron), non-ferrous (aluminum, copper), and stainless steel contaminants in food products. It is particularly effective for dry products like grains, spices, and snacks, as it can pick up even small fragments of metal, ensuring product safety and protecting machinery from damage.
How Does X-ray Inspection Work?
X-ray inspection systems use high-energy X-rays to pass through food products and detect contaminants based on density differences. Dense materials like metal, glass, bone, and stone absorb more X-rays and appear darker in the image, making them detectable. X-ray inspection also scans through packaging, which is beneficial when dealing with sealed or metalized packaging like cans or pouches. This technology offers broader contaminant detection and can also assess product quality by checking for missing items, underfill, or packaging defects.
Key Differences Between the Two Technologies
The primary difference between metal detection and X-ray inspection lies in their detection capabilities. Metal detectors are focused on identifying metals, especially ferrous and non-ferrous, while X-ray inspection can detect a wider range of contaminants, including non-metallic materials such as glass, plastic, and bone. X-ray inspection is better suited for products in metalized packaging, whereas metal detectors struggle with this. Additionally, X-rays are not affected by moisture, salt, or temperature, making them ideal for wet or conductive foods, unlike metal detectors that can experience false readings in these conditions.
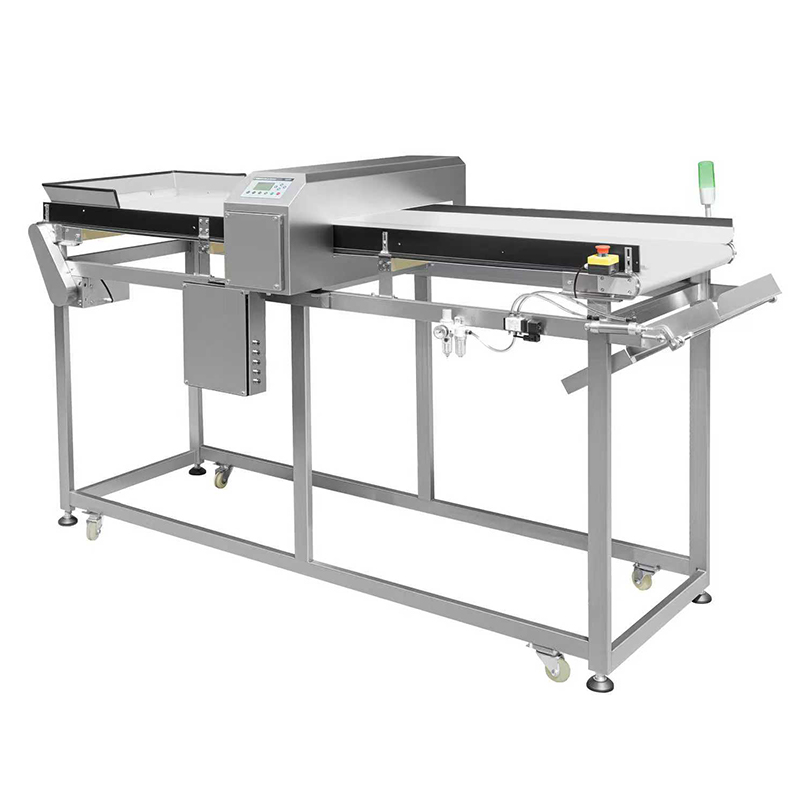

When to Use Metal Detection
Ideal for Detecting Metal Contaminants
Metal detection technology is primarily used for detecting metal contaminants in food processing. The following table outlines different metal detection systems, their applications, technical specifications, and key considerations to help you choose the right metal detection technology.
| Application Scenario | Metal Detection Technology Type | Detectable Metal Types | Technical Specifications | Key Considerations |
| Dry Food Products | High Sensitivity Metal Detectors | Ferrous, Aluminum, Copper, Stainless Steel | Sensitivity: Can detect metal as small as 0.5mm | Best for dry products like grains, spices, etc. |
| Packaged Foods | Conveyor Metal Detectors | Ferrous, Aluminum, Copper, Stainless Steel | High-frequency electromagnetic field, automatic alarm | Packaging can affect detection accuracy |
| Thin Metal Object Detection | Multi-Frequency Metal Detection Systems | All metal types | Multi-frequency scanning: Enhanced detection for thin metals | Suitable for products with thin metal packaging like foil |
| Machinery Protection | Heavy-duty Industrial Metal Detectors | Ferrous, Aluminum, Copper, Stainless Steel | High-strength anti-interference features, suitable for harsh environments | Installed at the beginning of the production line to protect machinery |
Tip: When using multi-frequency metal detection systems, it helps reduce interference and improves the detection accuracy of thin metals, especially in high-speed production environments.
Cost and Longevity Advantages of Metal Detectors
Metal detectors have a lower initial cost and tend to last longer, with many systems functioning efficiently for up to 20 years. Their simple design and robust construction make them a cost-effective option for facilities with tight budgets. Since metal detectors are easy to maintain and have fewer moving parts, they also offer a lower total cost of ownership over time.
Simple Products and Equipment Protection
In many food processing lines, metal detection is used early in the production process to ensure raw materials are free from metal contaminants before they are processed further. Metal detection also protects expensive machinery from damage caused by metal debris, which could lead to costly repairs and downtime. For small, dry food products, metal detectors provide a simple yet reliable inspection method.
When to Use X-ray Inspection
Broad Contaminant Range
X-ray inspection systems offer a broad range of contaminant detection capabilities. The table below provides details on X-ray inspection systems, including their applications, technical specifications, suitable products, and key considerations to help you choose the right X-ray inspection solution.
| Application Scenario | X-ray Inspection Technology Type | Detected Contaminants | Technical Specifications | Suitable Products | Key Considerations |
| Wide Contaminant Detection | High-energy X-ray Systems | Metals, Glass, Stone, Bone, Certain Plastics | Sensitivity: Can detect metal contaminants as small as 0.4mm | Various packaged foods, such as meat, dairy, pre-packaged meals | Avoid issues with low-density contaminants (e.g., wood) |
| Complex Packaging Foods | X-ray Scanning Systems | Metals, Glass, Stone, Bone, Plastics, Rubber | High penetration ability, suitable for metal packaging | Ready meals, bagged foods, metal can packaging | Ideal for metal-packaged foods (e.g., aluminum foil bags) |
| Wet or Conductive Foods | Dual-energy X-ray Systems | Metals, Glass, Bone, Stone, Plastics, Rubber | Unaffected by moisture, salt, or temperature variations | Seafood, meats, dairy, sauces, and other wet products | Effectively detects contaminants in high-moisture or high-salt foods |
| Quality Control Functions | High-speed X-ray Inspection Systems | Detects metals, non-metal contaminants, and fill levels | Automated quality control, can inspect packaging integrity | Canned foods, bagged snacks, confectionery | Provides fill-level and packaging integrity checks |
Tip: X-ray inspection is ideal for complex packaging and wet foods, especially when metal packaging interferes with metal detectors.
Handling Conductive or Wet Products
For products with high moisture or salt content—such as meats, cheeses, and seafood—X-ray inspection is more reliable than metal detectors. Metal detectors can struggle with these products due to their "product effect," where the conductive properties of the product interfere with the detection of metal contaminants. X-ray inspection, however, is not affected by the moisture or salt content, making it a more accurate solution for these types of foods.
Quality Control Beyond Contaminants
X-ray inspection systems do more than just detect contaminants. They can also perform various quality control tasks such as measuring fill levels, checking the integrity of seals, and counting the number of items in a package. These added capabilities make X-ray inspection an excellent choice for facilities that need to ensure product consistency and packaging quality along with contamination control.

How to Choose the Right Technology for Your Facility
Consider Your Product Type
The type of product you process is a critical factor in deciding whether to use metal detection or X-ray inspection. For example, dry, non-conductive products like rice or flour may only require metal detectors. In contrast, wet or conductive products, such as fresh meat or dairy, require X-ray inspection for accurate contaminant detection. Assessing the moisture, density, and packaging of your products will help determine which system works best for your facility.
The Role of Contaminants in Decision Making
If your primary concern is metal contamination, metal detectors are typically sufficient. However, if you need to detect a broader range of contaminants like glass or stones, X-ray inspection will be more effective. It's essential to consider the type of foreign materials that could potentially contaminate your food products when making your decision.
Budget Considerations
While metal detectors are generally more affordable and require less maintenance, X-ray systems offer additional features that may justify the higher initial cost. If your budget allows and you need the additional functionalities (such as quality control checks), X-ray inspection could be a worthwhile investment. However, for smaller operations or those focused on metal contamination, a metal detector may be a better fit.
Combining Metal Detection and X-ray Inspection for Comprehensive Safety
Layered Approach for Maximum Protection
For comprehensive safety, many food processing facilities use both metal detection and X-ray inspection in tandem. Metal detectors can be placed early in the production process to protect equipment from large metal debris, while X-ray systems can be used after packaging to detect a broader range of contaminants and perform additional quality checks.
Case Study of Effective Combined Use
In a facility processing packaged nuts, raw almonds are first screened with a metal detector to catch any large metal fragments from harvesting or transportation. After packaging, the products are run through an X-ray system to detect any remaining contaminants, including glass shards or stones. This dual inspection process ensures the highest level of safety for consumers.
Benefits of Dual Systems
Using both systems provides redundancy and ensures that no contaminants are missed. Metal detectors offer cost-effective and reliable detection for metals, while X-rays enhance detection capabilities by identifying non-metallic contaminants and verifying packaging integrity. This combination creates a robust food safety system.
Key Benefits of Each Technology
Advantages of Metal Detection
Metal detectors are increasingly equipped with advanced features like multi-frequency scanning, which enhances their ability to detect a wider range of metallic contaminants, even in challenging environments. They are highly effective in high-speed production lines and can be easily integrated into existing systems. Additionally, some modern metal detectors offer real-time data monitoring, providing valuable insights into system performance and contamination trends, which can help food manufacturers improve safety standards and operational efficiency.
Advantages of X-ray Inspection
X-ray systems have evolved to incorporate dual-energy technology, which provides enhanced sensitivity for detecting a broader spectrum of contaminants, including low-density materials. This advancement allows for better discrimination between contaminants and the product itself, reducing false rejects. Additionally, X-ray inspection plays a crucial role in quality control by measuring product weight, verifying fill levels, and ensuring package integrity, all of which contribute to maintaining product consistency and compliance with industry standards.
The Future of Detection Technologies
The future of food safety inspection lies in the integration of AI and machine learning into both metal detection and X-ray systems. These technologies will enable real-time adaptive detection, allowing systems to automatically adjust their sensitivity based on the product’s characteristics. As food manufacturers face increasing pressure to meet both food safety regulations and consumer demands for higher-quality products, these innovations will play a critical role in streamlining operations and reducing the risk of contamination while ensuring compliance.
Conclusion
Both metal detection and X-ray inspection are essential in food safety. Metal detection is ideal for identifying metal contaminants, particularly in dry products. On the other hand, X-ray inspection offers broader detection capabilities, identifying metals, glass, and other foreign materials, while also assisting with quality control. For comprehensive safety and efficiency, consider combining both technologies in your production line. This hybrid approach ensures thorough contaminant detection and maintains high-quality standards, ultimately protecting your brand and consumers. Companies like Dongguan COSO Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. provide advanced solutions that combine reliability with cost-effectiveness, ensuring both safety and operational efficiency in food processing.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between Metal Detection and X-ray Inspection in food processing?
A: Metal Detection identifies metallic contaminants like iron, aluminum, and copper using electromagnetic fields. X-ray Inspection, on the other hand, can detect metals as well as non-metallic contaminants like glass, bone, and plastic through density differences.
Q: When should I use Metal Detection over X-ray Inspection?
A: Metal Detection is best for detecting metal contaminants in dry products, such as grains and spices. It’s a cost-effective solution for food products that primarily face metal contamination risks.
Q: How does X-ray Inspection work in food processing?
A: X-ray Inspection uses high-energy X-rays to pass through food, detecting contaminants based on their density. It can find metals, glass, bones, and other foreign materials, even in sealed packaging.
Q: Which technology is better for wet food products: Metal Detection or X-ray Inspection?
A: X-ray Inspection is more effective for wet or conductive products, like seafood or dairy, as it is unaffected by moisture, salt, or temperature variations that can impact Metal Detection.
Q: How much does Metal Detection cost compared to X-ray Inspection?
A: Metal Detection is typically more affordable with lower initial and maintenance costs. X-ray Inspection systems have a higher upfront cost but offer broader detection capabilities and additional quality control functions.
 +86 15814116500
+86 15814116500