Introduction
Metal contamination in food products can cause serious health risks and costly recalls. Even tiny fragments of metal can damage a brand's reputation. Metal detectors are essential tools in preventing such issues. In this article, we will explore the different types of metal detectors used in food inspection. You'll learn about their benefits and the factors to consider when selecting the right system for your production line.
How Metal Detectors Work in Food Inspection
Electromagnetic Field Creation
Metal detectors use electromagnetic principles to detect contaminants by generating an electromagnetic field via a transmitter coil. This field interacts with the food product as it passes through the detector. The design of the electromagnetic field is calibrated to ensure balance, enabling precise detection. Disruptions in the field caused by metallic objects, regardless of size, trigger a response. The frequency of the generated field can be adjusted to detect different metal types, optimizing performance across various food products.
Detection of Metal Contaminants
When food passes through the electromagnetic field, any metal contaminant disrupts the field’s balance. The disruption causes a voltage fluctuation that the system detects. The receiver coils then capture these fluctuations, and digital processors analyze the signals. Advanced systems can differentiate between metals of varying properties, such as ferrous, non-ferrous, and stainless steel, ensuring the detection of even tiny particles. Technologies like multi-frequency detection help eliminate the effects of food properties, such as moisture or salt, on detection accuracy.
Signal Processing and Product Rejection
Once the voltage change is detected, the signal is processed by a sophisticated digital system that distinguishes between contamination and the food's natural elements. This processing involves advanced algorithms to filter out non-metallic interference, improving the accuracy of the system. If metal is confirmed, the detector triggers an automated rejection system, such as a pusher or air blast, to remove the contaminated product. These rejection systems are crucial in high-speed production environments, ensuring contaminated products are quickly separated without slowing down the production process.
Types of Metal Detectors Used in Food Manufacturing
metal detection systems are specifically engineered for the fast-paced bakery environment, ensuring the highest level of food safety for both raw dough and finished baked goods. Equipped with advanced multi-frequency sensors, these detectors provide real-time inspection for a wide variety of bakery products, including bread, pastries, biscuits, and cakes, whether packaged or moving loose on the belt.

It specifically engineered for products in aluminum foil pouches or trays, this metal detector overcome the challenges of "packaging effect." While traditional detectors are triggered by the foil itself, this advanced system utilizes magnetic field technology to accurately identify ferrous metal contaminants hidden inside. It is the ideal solution for metalized film snacks, foil-wrapped chocolates, and ready-to-eat meals, ensuring consumer safety and brand protection without compromising production speed.
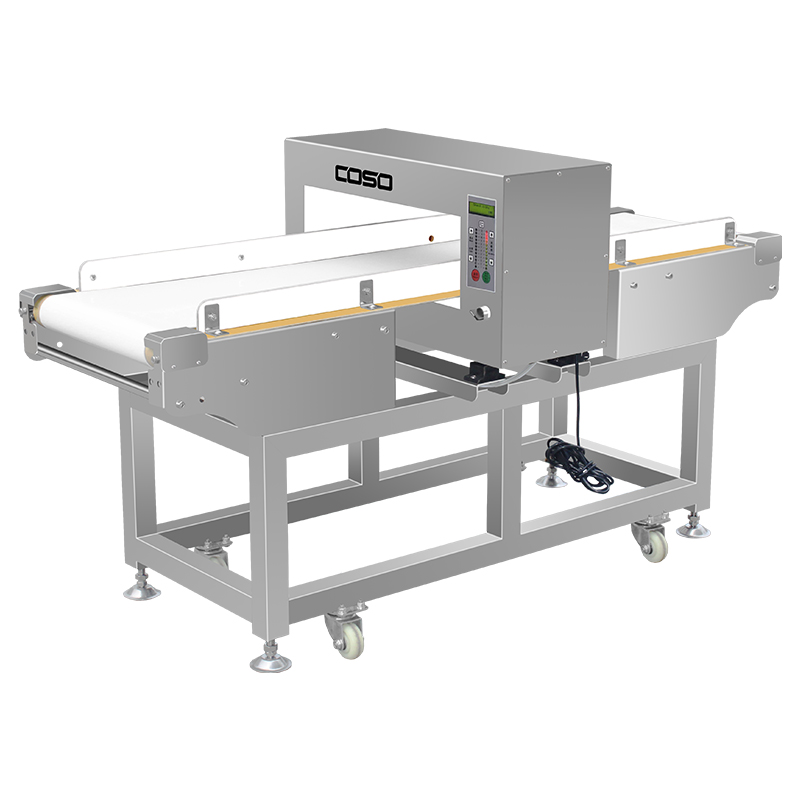

Our waterproof metal detectors are purpose-built for the extreme humidity and demanding hygiene requirements of the seafood and frozen food industries. Constructed from high-grade, corrosion-resistant stainless steel, these systems are designed for full washdown environments, allowing for thorough cleaning with high-pressure hoses after every shift. Equipped with advanced product effect compensation, the system maintains high sensitivity when inspecting salt-rich or high-moisture products, such as fresh fish, shrimp, and brined seafood.

Key Features to Look for in Food Metal Detectors
Sensitivity and Detection Size
The sensitivity of a metal detector is crucial for detecting even the smallest metal particles, especially non-ferrous metals which are often difficult to detect. The following table outlines important technical specifications for metal detectors in terms of sensitivity, along with their applications.
| Technical Specification | Description | Application Scenarios | Considerations |
| Detection Sensitivity | The detector's ability to detect small metal particles, usually measured in millimeters. | Foods requiring high sensitivity, such as meat, bakery items, and candy. | High sensitivity may cause false alarms; adjust according to the actual conditions. |
| Minimum Metal Particle Detection | The smallest metal particle size detectable, typically measured in millimeters. | Products with small metal particles, such as frozen foods, packaged snacks, etc. | Adjust the detector according to the size of the particles to avoid missing or false alarms. |
| Non-Ferrous Metal Detection | The sensitivity to non-ferrous metals, such as stainless steel, which are harder to detect. | Foods with high stainless steel content, such as dairy products, nuts, etc. | High sensitivity to non-ferrous metals ensures protection but may require additional settings. |
| Detection Accuracy | The accuracy of the detector under different temperature, humidity, or salinity conditions. | Foods with high salt, moisture, or mineral content, such as seafood or preserved foods. | Use multi-frequency technology to ensure accuracy and avoid false positives in challenging conditions. |
Tip: Make sure to adjust the sensitivity of the metal detector based on the type of food, production environment, and type of metal contamination to ensure optimal performance.
Overcoming Product Effect
Certain foods, such as those with high moisture, salt, or mineral content, can interfere with metal detectors, leading to false alarms. Advanced detectors use multi-frequency technology to overcome this “product effect” and reduce the risk of unnecessary rejections. This technology ensures that the detection system accurately identifies metal without being influenced by the food's characteristics.
Hygienic Design
Hygiene is a top priority in food manufacturing. Metal detectors should be constructed from stainless steel and designed for easy cleaning. This ensures that the equipment remains compliant with food safety standards, such as HACCP, and prevents the buildup of contaminants that could affect food safety.
Benefits of Using Metal Detectors for Food Safety
Ensuring Consumer Safety
Metal detectors play a vital role in ensuring consumer safety by preventing harmful metal fragments from entering food products. These fragments can cause choking or internal injury if consumed, making the detection and removal of contaminants essential for protecting public health.
Compliance with Regulations
Food manufacturers are required to meet strict regulations, such as those set by the FDA and USDA, regarding food safety. Metal detectors help companies comply with these standards by ensuring that metal contaminants are detected and removed from products. This not only helps prevent legal liabilities but also ensures a safer food supply chain.
Protecting Brand Reputation
A single instance of metal contamination in food can lead to costly recalls and long-term damage to a brand's reputation. By investing in a metal detection system, manufacturers can prevent such incidents and maintain consumer trust. Consistently safe products contribute to positive brand recognition and customer loyalty.
Advanced Features and Technologies in Metal Detection
Multi-Spectrum and Multi-Frequency Detection
Multi-frequency and multi-spectrum detection technologies enhance the performance of metal detectors, especially in complex environments, helping to overcome "product effect" interference. The following table summarizes the key advantages of these technologies and their suitable applications.
| Technical Feature | Description | Application Scenarios | Considerations |
| Multi-Frequency Detection | Uses multiple frequencies to detect various types of metals simultaneously, increasing sensitivity. | Ideal for wet, salty, or mineral-rich foods, such as meat, dairy, etc. | Reduces interference from "product effect" but may need regular calibration to maintain accuracy. |
| Multi-Spectrum Technology | Scans multiple wavelengths to detect both metallic and non-metallic contaminants. | Used for packaged foods, especially liquids, solids, and food packaging materials (e.g., aluminum foil). | Must be finely tuned to avoid missing contaminants or generating false alarms. |
| Adaptive Sensitivity Adjustment | Automatically adjusts sensitivity to adapt to different food compositions and detection needs. | Suitable for diverse production lines, such as freeze-dried foods, baked goods, etc. | Consider environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and salinity when adjusting sensitivity. |
| Anti-Interference Technology | Prevents false positives or missed detections caused by the product's salt, moisture, or mineral content. | Used for foods with high mineral content or other special properties, such as salty foods, pickled products, frozen items. | Regular maintenance and recalibration are necessary to ensure consistent performance. |
| Detection Depth vs. Accuracy | Balances detection depth and sensitivity to ensure accurate results without affecting production speed. | Ideal for high-speed production lines, such as ready-to-eat foods or baked products. | Find the best balance between detection depth and accuracy to avoid disrupting production flow. |
Tip: For handling high moisture, salt, or mineral-rich foods, choose a metal detector with multi-frequency and multi-spectrum capabilities to effectively overcome "product effect" and improve detection accuracy.
Automatic Rejection Mechanisms
Modern metal detectors are often equipped with automatic rejection systems, such as push lever rejection, pusher rejection, belt sinking rejection, air blow rejection, flap rejection. These systems automatically remove metal contaminants from the production line, preventing them from reaching consumers. This automatic action improves efficiency and ensures that the detection process does not slow down production.
Integration and Data Logging
For food manufacturers, it's essential to have metal detection systems that seamlessly integrate into existing production lines. Furthermore, advanced systems offer data logging features that record inspection data, providing traceability and helping companies with audits and compliance. These features ensure that food manufacturers meet regulatory requirements while maintaining efficient operations.
Choosing the Right Metal Detector for Your Food Production Needs
Considerations for Food Type and Contaminant Size
When choosing a metal detector, consider the type of food being processed and the size of the metal contaminants. For example, if you're processing dry products, a conveyor metal detector might be the best option, while bulk food processing could require a gravity-fed system. The right detector will address specific contamination risks and provide the most efficient solution.
Sensitivity vs. False Rejects
Balancing the sensitivity of a metal detector with the potential for false rejects is crucial for maintaining a smooth production line. High sensitivity ensures contaminants are detected, but it can also lead to false rejections of perfectly good products. It is important to choose a system that offers adjustable sensitivity levels to minimize false alarms while maintaining safety.
Cost and Maintenance
While metal detectors are an investment, their long-term benefits in terms of consumer safety, regulatory compliance, and brand protection make them essential. Consider both the initial cost and ongoing maintenance when selecting a system. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of the detector.
Conclusion
Metal detectors are critical in ensuring food safety by detecting harmful contaminants, safeguarding consumers, and protecting brand reputation. Different systems, such as conveyor and pipeline detectors, cater to various food production needs. By selecting the appropriate metal detection solution, food manufacturers can prevent costly contamination issues and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Dongguan COSO Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. offers advanced metal detection systems that enhance product safety and streamline production processes, providing valuable solutions for food manufacturers.
FAQ
Q: What is a Metal Detector for food inspection?
A: A metal detector for food inspection is a device used to detect metal contaminants in food products. It helps ensure food safety by identifying ferrous, non-ferrous, and stainless steel particles during the manufacturing process.
Q: How does a Metal Detector work in food processing?
A: Metal detectors create an electromagnetic field, which scans food products. When a metal object disrupts the field, the system alerts and removes the contaminated product, ensuring safe food production.
Q: Why is a Metal Detector essential in food safety?
A: Metal detectors prevent harmful metal fragments from entering food, reducing health risks, costly recalls, and damage to a brand’s reputation. They help manufacturers comply with food safety regulations.
Q: What types of Metal Detectors are used in food manufacturing?
A: The most common types are conveyor metal detectors, gravity-fed detectors for bulk items, and pipeline detectors for liquids and pastes. Each is designed for specific food processing needs.
Q: How much does a Metal Detector for food inspection cost?
A: The cost of a Metal Detector depends on the system’s features, such as sensitivity and detection type. Prices can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars depending on the complexity and application.
 +86 15814116500
+86 15814116500